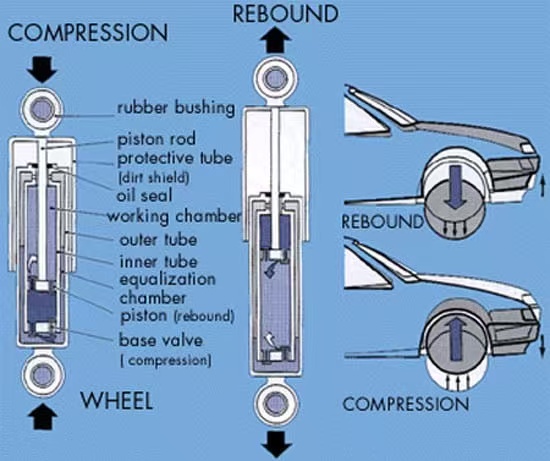
Shock absorber (or damper) is a critical component of a vehicle’s suspension system. Its primary function is to absorb and dissipate kinetic energy generated by road irregularities or dynamic loads, ensuring ride comfort and stability.
Key Components:
1. Piston & Piston Rod: Connects the wheel to the vehicle body, moving vertically with vibrations.
2. Hydraulic Fluid/Gas: Fills the cylinder and flows through valves to create damping resistance.
3. Valve System: Controls fluid flow rate to generate adjustable damping forces.
Operation Process:
1. **Compression Stroke** (Wheel upward motion):
- The piston moves downward, compressing fluid in the lower chamber.
- Fluid flows through small orifices/valves in the piston, generating resistance to cushion impacts.
2. Rebound Stroke (Wheel downward motion):
- The piston moves upward, forcing fluid from the upper chamber back to the lower chamber.
- Valves are designed to provide higher resistance during rebound than compression, preventing excessive body oscillation.
Conclusion: By converting kinetic energy into heat through controlled fluid damping, shock absorbers minimize vibrations, enhance ride quality, and maintain tire contact with the road.